PYTHON BASIC TOPICS
 PYTHON
PYTHON
Introduction:-
Python is an popular programming language.It was created by Guido Van Rossum,and released in 1991.It supports object oriented programmming approach to develop applications.
It is used for:
=>Web development
=>software development
=>system scripting
$ Python is processed at run time by interpreter.
$ The line which starts with >>>, is known as python prompt.
Advantages or characteristics of python or why python? :-
$ Python works on different platforms(windows,linux,mac,etc..).
$ python has simple syntax similar to english language.
$ Python is easy to learn yet powerful and versatile scripting language.
$ Python supports multiple programming pattern,including object oriented,imperative and functional or procedural programming styles.
$ We don't need to use data types to declare variable because it is dynamically typed.
$ Python makes the development and debugging fast because there is no compilation step included in python development and edit-test-debug cycle is very fast.
Features of python:-
1.Easy to learn and use.
2.Expressive language.
3. Object oriented language.
4.Extensible.
5.Large standard library.
6.GUI programming support.
7.Integrated.
8.Interactive mode.
9.Data bases.
HELLO WORLD PROGRAM
>>>print("Hello World!")
Hello World
Python Variables:-
A variable in programming is used to store data(values).
EXAMPLE
X=5
Y="FAIZU"
print(X) #5
print(Y) #FAIZU
Data types:-
Text type:str
Numeric types:int,float,complex
Sequence types:list,tuple,range
Mapping types:range
Set types:set,frozenset
Boolean types:bool
Binary types:bytes,bytearray,memoryview
EXAMPLE
x="Hello world" str
x=20 int
x=20.5 float
x=1; complex
x=["Red","blue","green"] list
x=("Red","blue","green:) tuple
x=range(6) range
x={"name":"John","age":36} dict
x={"Red"."blue","green"} set
x=frozenset({"Red","blue","green"}) frozenset
x=True bool
Python Numbers:-
=>int
=>float
=>complex
EXAMPLE
x=1 #int
x=2.8 #float
x=1j #complex
Keywords in python:-
There is one more restriction on identifier names.No object can have the same name as a reserved word.
==>False,class,finally,is,return,none,continue,for,lambda,try,True,def,from,nonical,while,and,del,global,not,with,as,elif,if,or,yield,assert ,else,else,import,pass,break,except,in,raise are the keywords.
Python Identifiers:-
An identifier is a name given to entities like class,functions,variables,etc.
Rules for writitng identifiers:
=>we can use (a to z),(A to Z),(0 to 9),underscore(_).
=>An identifier cannot start with a digit.
=>keywords cannot be used as identifiers.
=>we cannot use special symbols like !,@,$,%,%,etc.
=>Identifier can be of any length.
Python Operators:-
Operators are special symbols in python that carry out arithmetic or logical computation.The value that the operator operates is called the operands.
Arithmetic Operator:
Addition:
>>>2+3
5
Subtraction:
>>>3-2
1
Multiplication:
>>>3*2
6
Division:
>>>3//2
1.5
=>The arithmetic operators are +,-,*,/,%,//,**.
Comparision operators:
The comparision operators are >,<,==,!=,>=,<=.
Logical operators:
The logical operators are AND,OR,NOT.
AND-True if both the operands are true.
OR-True if either of the operands are true.
NOT-True if the oprand is false.
Bitwise operators:-
Bitwise AND(&),Bitwise OR(|),bitwise NOT(~),Bitwise XOR(^),Bitwise right shift(>>),Bitwise left shift(<<)
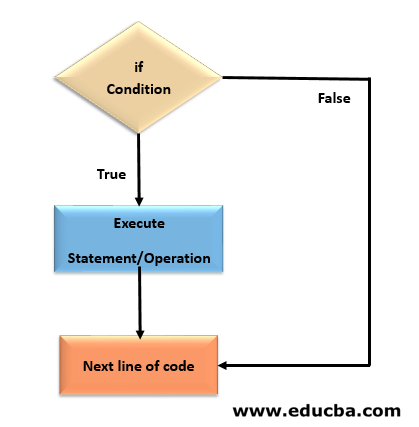
Conditional statements:-
If statement:
if statement evaluates whether a statement is true or false and executes the code only when the given condition or statement is true.
syntax:
if(condition):
statements
flowchart :
EXAMPLE
>>>grade=70
>>>if grade>=70:
>>> print("passed") #output:passed
If-else statement:
, if-else statement evaluates that if the condition is either true or false.If the condition is true then it executes the if statement otherwise it executes the else statement and ends the program.
syntax:
if condition:
statement
else:
statement
Flowchart:

EXAMPLE
>>>grade=60
>>>if grade>60:
>>> print("passed")
>>>else:
>>> print("fail") #output:passed
If-elif-else or else-if statement:
Syntax:
if condition:
statement
elif condition:
statement
else:
stetement
Flowchart:
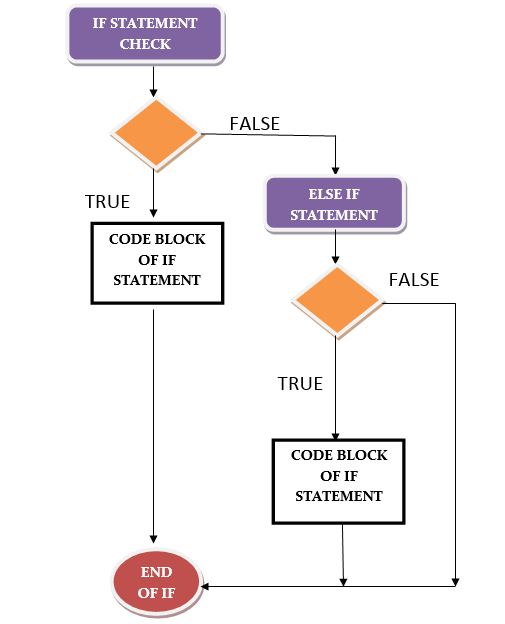
Explanation: The Flow starts with a if statement check, if the statement check fails then the control flows to the else if statement check, when the else if statement check evaluates as true then the flow goes to body of the else if statement.
Nested if statement:-
Nested if statement is used when we want to check for a secondary condition if the first condition executes as true.For this,we can have an if-else statement inside of another if-else statement.
syntax:
if condition:
statement
if condition:
statement
else:
statement
else:
statement
Flowchart:
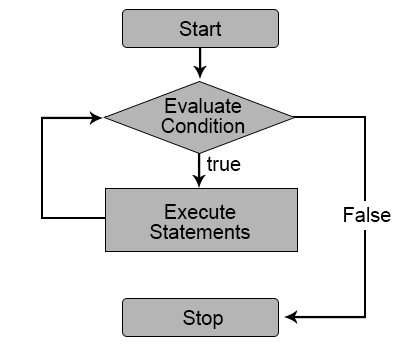
Loops in python:
While loop:
syntax:
while condition:
# execute these statements
else:
# execute these statements
EXAMPLE
>>>n=1
>>>print("Infinite loop starts")
>>>while n>0:
>>>n=n+1
>>>print(n)
output:
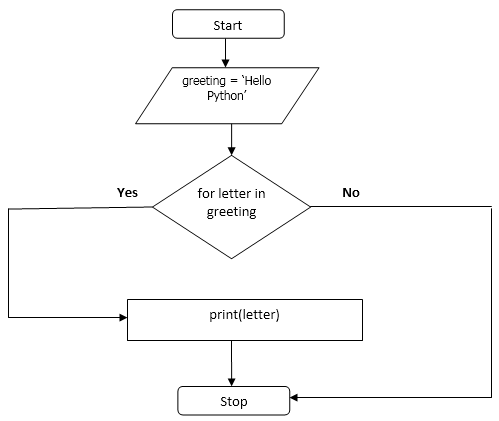
For loop:
For loops in python are designed to loop over any sequence like list, tuple, dictionary, set and string.
Syntax:
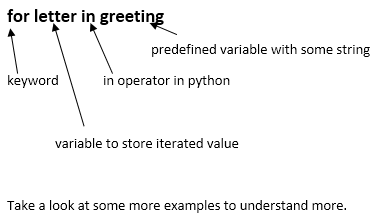
for [variable] in [sequence]
EXAMPLE
>>>greeting = ‘Hello Python’
>>>for letter in greeting:
>>> print(letter)
output:
![]()
Flowchart:
EXAMPLE
>>>sum=0
>>>for n in range(1,11):
>>> sum+=n
>>>print(sum)
output:
55
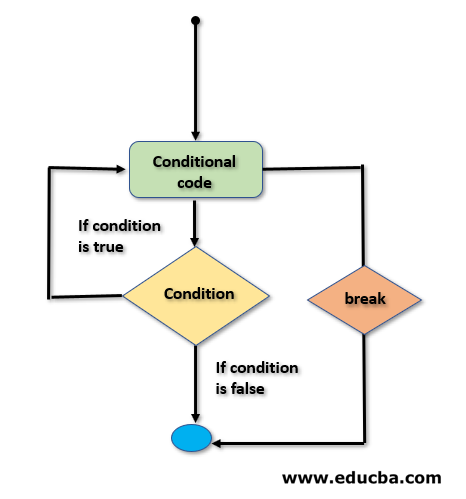
Python break:
The Break Statement is a simple statement that holds the power of terminating the normal flow of the group of statements.
Flowchart :


EXAMPLE
>>>a=[‘a’,’b’,’1’]
for I in a;
>>>if (i.is_numeric()):
>>>break
>>>print a
>>>print ‘Found a number in the list’
Output:
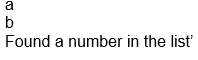

Comments
Post a Comment